Board members play a key position in guaranteeing their organisations are protected in opposition to cyber threats. They’re liable for setting the tone on the high and guaranteeing that cyber safety is prioritised on the highest ranges of the organisation. Authorized and moral obligations demand that board members keep knowledgeable concerning the cyber safety panorama and the particular dangers going through their organisations.
Failure to adjust to cyber safety rules can result in extreme penalties, together with substantial monetary penalties, authorized motion and irreparable injury to the organisation’s popularity. Current incidents have demonstrated that board members may be held personally accountable for lapses in cyber safety, going through each authorized and reputational dangers.
A devastating instance can be the case of Uber’s former safety chief, Joe Sullivan, who was convicted for concealing an information breach. In accordance with an affidavit reported by Courthouse News Service (2022), Craig Clark, an in-house lawyer at Uber, testified that this secrecy was accepted by the “A-Crew”, which included ex-CEO of Uber, Travis Kalanick, who knew and accepted the cost of a ransom to the hackers, which finally led to Uber being fined $148 million by the state as acknowledged by the Federal Trade Commission (2018). This case highlights the intense implications of neglecting cyber safety obligations. It’s important for board members to champion sturdy cyber safety practices and guarantee ample sources are allotted to safeguard their organisations. The potential repercussions of non-compliance ought to function a stark warning to those that underestimate the significance of cyber safety.
Cyber threats are not a distant chance however an imminent and fixed actuality. With every passing day, these threats develop extra refined and damaging, forcing organisations to urgently strengthen their defences and governance buildings to outlive in an more and more dangerous digital surroundings. Excessive-profile breaches, akin to these skilled by the Government Employees Pension Fund and TransUnion, underscore the damaging influence of cyber assaults, which lead to substantial monetary losses, erode buyer belief and injury reputations. In 2021, the Council for Scientific and Industrial Analysis (CSIR) estimated the impact of cyber crime on South Africa’s economy at R2.2 billion per annum. South African corporations, among the many high eight targets for ransomware assaults, have seen incidents affecting credit score bureaus, healthcare, retail teams, authorities departments and banks. The complexity of cyber threats necessitates a proactive, multilayered defence technique that includes the most recent applied sciences and finest practices, alongside fostering a tradition of safety consciousness to minimise the chance of human error.
Developments driving demand for governance in cyber safety
Knowledge privateness has emerged as a central theme in lots of latest high-profile cyber safety assaults, pushing governance officers to the forefront of political, financial and technological discussions. This wave has highlighted the essential position of cyber professionals who can successfully interact within the worldwide safety dialogue.
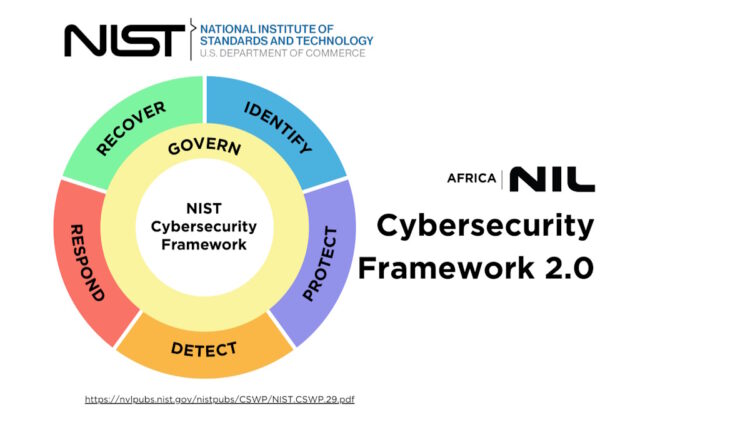
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has updated its framework to version 2.0, now incorporating governance, which underscores the necessity for sturdy governance and compliance practices.
In South Africa, the Monetary Sector Conduct Authority (FSCA) and the South African Reserve Financial institution (SARB) have issued a Joint Standard requiring monetary establishments to adjust to cyber resilience measures by November 2024.
By the top of subsequent 12 months, three-quarters of the world’s inhabitants will likely be lined by information privateness legal guidelines, reflecting the worldwide shift in the direction of stringent data protection measures (ISC2, 2024). These world and native developments are driving the firming of cyber safety governance, making it a important space for organisations to deal with.
Addressing danger, compliance, governance
Efficient cyber safety governance entails a mix of danger administration, compliance adherence and strategic oversight. Organisations should implement sturdy danger administration methods to establish, assess and mitigate potential threats. This contains common danger assessments, incident response planning and steady monitoring of the menace panorama.
A serious enhancement to the NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) is the addition of the brand new Govern Operate, which underscores the significance of governance in managing cyber safety dangers. This Govern Operate is now central to the framework and informs the implementation of the opposite 5 capabilities. It highlights that cyber safety needs to be thought-about a big enterprise danger, alongside monetary and reputational dangers.
NIST framework.
The up to date framework is structured round six key capabilities:
- Govern: Set up and oversee the organisation’s cyber safety danger administration technique, expectations and insurance policies.
- Determine: Decide the present cyber safety dangers to the enterprise.
- Defend: Implement safeguards to stop or mitigate cyber safety dangers.
- Detect: Determine and analyse potential cyber safety threats and breaches.
- Reply: Take motion in response to detected cyber safety incidents.
- Get well: Restore any belongings and operations affected by a cyber safety incident.
Moreover, the brand new Govern Operate ensures that the implementation of CSF 2.0 is sustainable for organisations by specializing in governance classes akin to:
- Organisational context (GV.OC): Addresses the organisation’s danger administration choices.
- Oversight (GV.OV): Encourages steady enchancment and changes to the organisation’s danger administration technique.
- Danger administration technique (GV.RM): Helps operational danger choices primarily based on the organisation’s danger tolerance, urge for food statements, assumptions and different elements.
- Roles, obligations and authorities (GV.RR): Defines roles and obligations to foster steady enchancment and constant efficiency assessments (NIST, 2024).
Sturdy governance buildings be sure that cyber safety is built-in into the organisation’s general technique. This entails defining clear roles and obligations, fostering a tradition of accountability and guaranteeing that cyber safety issues are embedded in all enterprise choices.
NIL Africa and ISC2 partnership: A strategic transfer
In response to those challenges, NIL Africa has partnered with ISC2 to launch a Cyber Safety Governance programme. This complete programme takes professionals from zero to CGRC licensed with CC certification and CGRC certification. It additionally contains additional modules masking worldwide and South African cyber legislation content material.
The programme is geared toward:
- Data safety groups
- Danger administration groups
- Compliance groups
- IT governance groups
- Inside audit groups
- Knowledge governance groups
- Enterprise continuity/catastrophe restoration groups
- Authorized and regulatory groups
- Company governance groups
- Third-party danger administration groups
The primary cohort begins this 12 months in 2024.
NIL Africa, recognized for its revolutionary options and dedication to IT coaching excellence, and ISC2, a globally recognised chief in cyber safety certification, deliver collectively their experience to create a complete programme geared toward enhancing cyber safety governance expertise in organisations. This partnership seeks to equip organisations with the instruments and data wanted to navigate the altering panorama of governance, danger and compliance in cyber safety. By combining NIL Africa’s sensible expertise with famend facilitators and instructors with ISC2’s instructional sources, this initiative goals to make a big influence within the battle in opposition to cyber crime and compliance.
Potential members and organisations focused on enrolling within the Cyber Safety Governance Programme or searching for further info are inspired to contact a NIL Africa gross sales consultant or e-mail gross [email protected] for additional particulars.
References
Courthouse Information Service, 2022. Fired Uber lawyer testifies in opposition to ex-security chief in trial over 2016 information breach cover-up. [online] Out there at: https://www.courthousenews.com/fired-uber-attorney-testifies-against-ex-security-chief-in-trial-over-2016-data-breach-cover-up/ [Accessed 20 May 2024].
Federal Commerce Fee, 2018. Federal Commerce Fee Offers Ultimate Approval to Settlement with Uber. [online] Out there at: https://www.ftc.gov/news-events/news/press-releases/2018/10/federal-trade-commission-gives-final-approval-settlement-uber [Accessed 20 May 2024].
Authorities Pensions Administration Company. (n.d.). Dwelling. Out there at: https://www.gpaa.gov.za/ (Accessed: 23 Could 2024).
Worldwide Telecommunication Union (ITU), 2021. World Cybersecurity Index (GCI) 2020. [online] Out there at: https://www.itu.int/hub/publication/d-str-gci-01-2021/ [Accessed 20 May 2024].
ITWeb, 2022. Inforeg slaps TransUnion with enforcement discover. [online] Out there at: https://www.itweb.co.za/article/inforeg-slaps-transunion-with-enforcement-notice [Accessed 20 May 2024].
ITWeb, 2023a. Cyber crimes annual influence on SA estimated at R22bn. [online] Out there at: https://www.itweb.co.za/article/cyber-crimes-annual-impact-on-sa-estimated-at-r22bn/JN1gPvOAxY3MjL6m [Accessed 20 May 2024].
ITWeb, 2023b. Monetary companies should transfer to adjust to new requirements for cyber resilience. [online] Out there at: https://www.itweb.co.za/article/financial-services-must-move-to-comply-with-new-standards-for-cyber-resilience/LPp6V7rBnoK7DKQz [Accessed 20 May 2024].
South African Reserve Financial institution, 2023. Publication of the Joint Normal IT Gov and Danger. [online] Out there at: https://www.resbank.co.za/en/home/publications/publication-detail-pages/prudential-authority/pa-public-awareness/Communication/2023/Joint-Communication-4-of-2023-Publication-of-the-Joint-Standard-IT-Gov-and-Risk [Accessed 20 May 2024].
(ISC)², 2024. What’s trending in GRC? [online] Out there at: https://www.isc2.org/Insights/2024/02/whats-trending-in-GRC?queryID=645ba836d4e2f0fe53d17fd1ba63545f [Accessed 20 May 2024].